(中文版本見後)
I re-rooted the whole sequence phylogenetic tree of Covid-19 (2019-nCoV; SARS-CoV-2). The phylogeny shows up that the most recent common ancestor (MRCA) might be circulating in human several months before the outbreak in Wuhan in Dec. 2019; the outbreak might be related to a non-synonymous Ser > Leu mutation in ORF8.
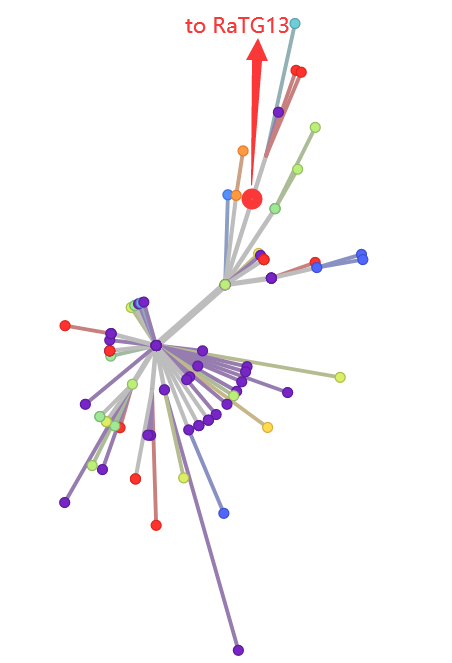
The auspice site collected dozens of whole genomic sequences of Covid-19, and made good visualization for the phylogeny. The webside put the node of the biggest “star cluster” as the beginning as the outbreak, which are commonly believed as the origin of the prevalence of this plague. However, this phylogenetic tree is unrooted. Since the mutation rate of a virus may not be in accordance with molecular clock assumption, the most recent common ancestor, or the “entrance of the tree” (e.g. “Y-chromosomal Adam” or “mitochondrial Eve” of modern human) should be confirmed through outgroup sequences. As the human Y chromosomal and mitochondrial trees were rooted using chimpanzee or Neanderthal sequences, naturally the closest strain to Covid-19, RaTG13, which was found in a bat in Yunnan province was applied for the re-rooting.
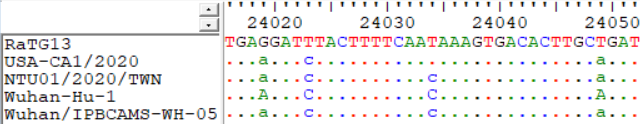
I discovered that the largest “star cluster” was not the MRCA of Covid-19! The root is shown in red in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2. Three mutations, C8782T (Fig. 3), T28144C (Fig. 4) and C24034T (Fig. 5) are found identical between bat coronavirus RaTG13 and those Covid-19 on the right of Fig. 2, but different to the others. So the root should be located at the position in red (although no sequence was found at this position, the closest sequence is one mutation away). A T>C muation at pos. 24034 caused a non-synonymous Ser > Leu change, which might cause the enhancement of the virulence. Also the rooting implies that Wuhan could be not the only candidate where the origin infection among human occurred; the virus circulation might have last a few weeks before December of 2019, but only known by human due to the rising of virulence in Wuhan. Future investigation of those sequences near the root might reveal hints for the origin of Covid-19.



我有了個重大發現:所有本次新冠病毒的共祖可能早在12月之前的數月;在武漢的爆發也許與一個蛋白突變有關。
大概說一下:這個网站 ,收集了幾十條新冠病毒的全序。网站把武漢最大的一個星簇作爲最左,同時一般也以爲這個是時閒最早。但以我對Y染色體和線粒體的經驗,最大的擴張處未必是最早的節點。這個其實是棵無根樹。尤其因爲病毒的演化速率會不符合分子鐘假設,而無根樹最早分化的節點(如“Y染色體亞當”和“線粒體夏娃”)需要通過outgroup來定根。現代人的Y染色體和線粒體可以用黑猩猩或尼安德特人來定根,而新冠病毒我自然想到用和其最接近的雲南蝙蝠冠狀病毒RaTG13來定。
結果,我發現最大的那個餅並不是樹根!眞正的樹根其實是在圖1和圖2標紅的位置。有三個突變,C8782T(圖3),T28144C(圖4),C24034T(圖5),RaTG13都是和圖2偏右的樣本一致。說明整個新冠肺炎的始祖是在紅叉處(但截至目前並沒有測到過序列全同的樣本,最少的也是差一步)。而ORF8(某個被翻譯的蛋白)上的T>C突變造成了一個絲氨酸到亮氨酸(Ser > Leu)的殘基改變,有可能是病毒毒力增強的重要位點。同時還說明,武漢有可能不是病毒的原發地,12月之前該病毒在人閒已經傳播數月,只是在武漢因毒力增強爆發纔爲人所知。最接近樹形眞正根部的這些樣本也許能提供病毒最初來源的更多線索。
順道說一下,中南大學的黃石敎授,爲什麼說人類的共祖不在亞洲而是非洲,就是因爲你定根定錯了!






